What is contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with an irritant or an allergen. It manifests as red, itchy, and sometimes swollen skin, and can vary in severity depending on the cause and individual sensitivity.
Types of Contact Dermatitis
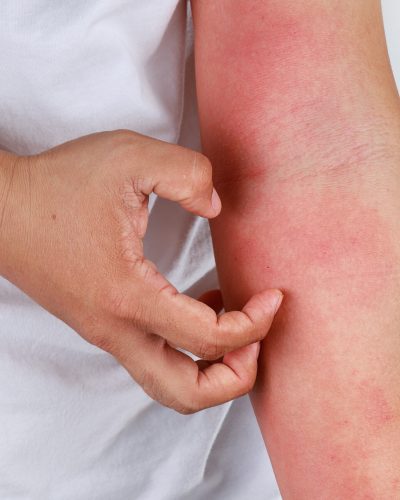
Irritant Contact Dermatitis
This is the most common form and occurs when the skin is exposed to substances that physically damage the skin barrier.
Common irritants include:
- Soaps and detergents
- Cleaning productsSolvents or chemicals
- Prolonged exposure to water
The reaction typically develops quickly after exposure and can cause dryness, scaling, and redness.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
This occurs when the immune system reacts to a substance (allergen) that comes into contact with the skin. The reaction might not appear until hours or even days after exposure.
Common allergens include:
- Nickel (in jewelry, watches, etc.)
- Fragrances and perfumes
- Latex
- Poison ivy, poison oak, or other plants
Allergic contact dermatitis can lead to more severe itching, swelling, and sometimes blistering.
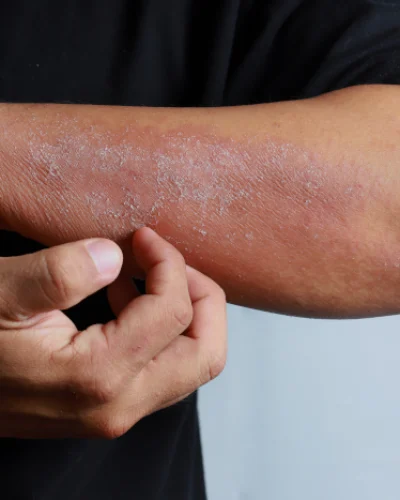
What are the symptoms of contact dermatitis
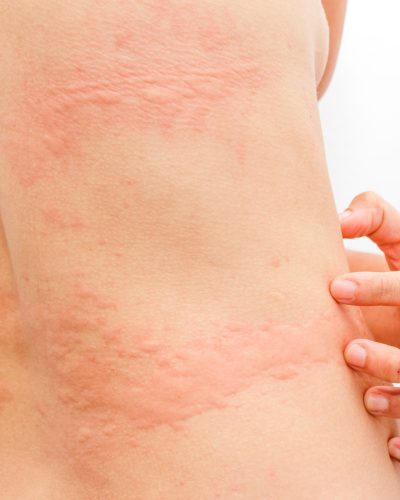
What are the symptoms of contact dermatitis
- Redness
- Itching
- Swelling
- Dry, cracked, or scaly skin
- Blisters (in more severe cases)
What causes contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis can be triggered by a wide range of substances. In some cases, it can develop after a single exposure, while in others, it occurs after repeated exposure over time.


How is contact dermatitis treated
Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding the irritant or allergen is crucial.
Topical Steroids: These can help reduce inflammation and itching.
Moisturizers: To restore the skin barrier and prevent further irritation.
Antihistamines: May be used for allergic contact dermatitis to reduce itching.
Medicated Creams: In severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications.
How is contact dermatitis prevented
- Wear protective clothing or gloves when handling irritants.
- Use fragrance-free, gentle skincare products.
- Avoid known allergens if you have a history of reactions.

Patch Testing
Patch testing is a diagnostic tool used to identify substances that may be causing allergic contact dermatitis. It helps pinpoint specific allergens by exposing small areas of skin to potential triggers in a controlled manner. The test does not check for irritant contact dermatitis but is focused on allergic reactions.
How Patch Testing Works
Consultation
Before the test, the dermatologist or allergist will discuss your medical history and any symptoms to determine which substances (allergens) to test. Common allergens include metals, fragrances, preservatives, and chemicals found in everyday products.
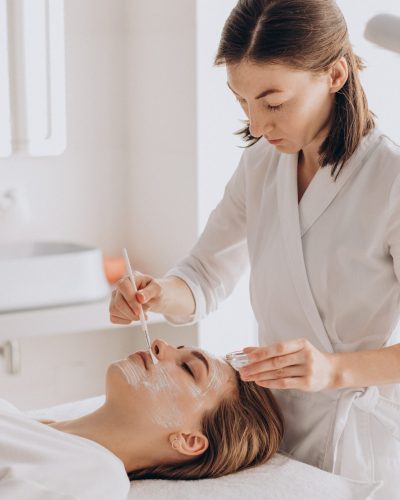

Application of Patches
Small amounts of potential allergens are applied to the skin using patches, which are adhesive strips with chambers that hold the test substances. These patches are usually placed on the upper back or arms. Typically, 20 to 30 substances are tested at one time.
Waiting Period
The patches remain in place for 48 hours. During this time, you should avoid activities that could cause the patches to move or become wet, such as vigorous exercise or showering.


First Reading (48 Hours)
After the 48-hour period, the patches are removed by the healthcare provider, and the skin is examined for any signs of an allergic reaction, such as redness, swelling, or small blisters.
Second Reading (72 to 96 Hours)
Because allergic reactions can take time to fully develop, a second reading is done a few days after the patches are removed, typically 72 to 96 hours after initial application. This helps identify any delayed reactions.


How are patch tests read
No reaction: Indicates that the skin did not react to the allergen.
Mild reaction: Slight redness or irritation, suggesting a low sensitivity to the allergen.
Moderate to severe reaction: Significant redness, swelling, or blistering indicates a clear allergic response to that substance.
What are the benefits of Patch Testing
Helps identify the specific allergen causing the contact dermatitis.
Allows patients to avoid triggers in the future, reducing the risk of flare-ups.
Can lead to better management of chronic dermatitis.


What are the limitations of patch testing
Patch testing can only detect allergic contact dermatitis, not irritant contact dermatitis.
Results may not be immediate and can require follow-up visits.
Some reactions may not appear during testing, even if the allergen is a trigger.
Dr. Weiss and the team at Trillium Dermatology rely on patch testing as it is a highly effective way to identify the root cause of allergic contact dermatitis, guiding patients in avoiding harmful substances and improving their skin health.
Embark on your journey to radiant skin
Raleigh dermatology patients who suffer from contact dermatitis, can schedule an appointment with us here. A member of our elite dermatology team, including Dr. Weiss, a nationally recognized contact dermatitis expert, will conduct a total evaluation of your skin. Our expert dermatology specialists will explore the various treatment options so that we give you the best treatment for your eczema. Patients with contact dermatitis, looking for a dermatologist near Hillsborough, Carrboro, Raleigh, Sanford, Mebane, Apex, Holly Springs, Durham, Burlington, Cary, and Alamance, can call our center for dermatology in Chapel Hill today to learn more.

