Eczema is a very common skin condition. Yet, patients struggle to find effective treatments because they cannot find a dermatology appointment. We understand the frustration of atopic dermatitis. At Trillium Clinic Dermatology in Chapel Hill, our solutions are designed to help Chapel Hill dermatology patients find a good eczema treatment. Dr. Weiss is a member of the National Eczema Association. He is considered in expert in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. With all of the available advanced dermatology treatments for eczema, the Chapel Hill dermatologists at Trillium Clinic Dermatology will help you get your eczema under control. Start an advanced atopic dermatitis treatment today!
What is Atopic Dermatitis
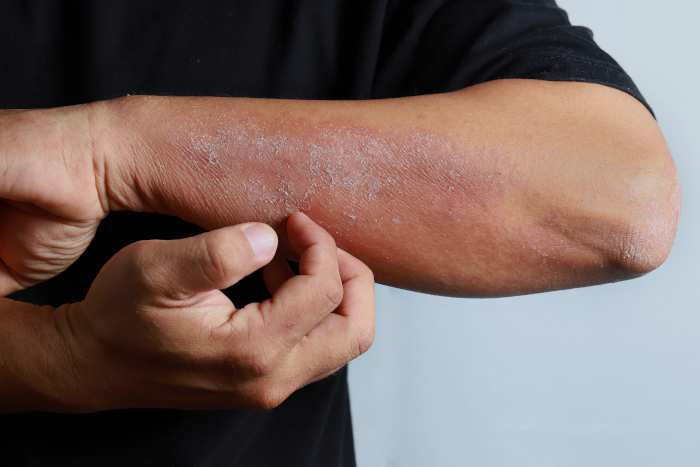
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that is characterized by itchy, red, and inflamed patches of skin. It is often seen in individuals with a personal or family history of allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever. Atopic dermatitis typically begins in infancy or childhood and can persist into adulthood.
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Factors such as a compromised skin barrier, immune system dysfunction, allergens, irritants, and emotional stress can trigger and exacerbate the symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
How is Atopic Dermatitis treated
People with atopic dermatitis might need to use special creams or ointments on their skin to make it better. They might also need to avoid things that can make their skin worse, like certain soaps or fabrics. Sometimes, doctors might prescribe special medicines to help with the itching and inflammation. It’s important to remember that atopic dermatitis can come and go, but there are things you can do to help take care of your skin and make it feel better.
There are different treatments available for atopic dermatitis. Here are a few examples:
Avoiding triggers: People with atopic dermatitis may need to avoid certain things that can make their skin worse, such as harsh soaps, certain fabrics, or specific allergens like pet dander or pollen.
Moisturizers: Keeping the skin moisturized is very important in managing atopic dermatitis. Using moisturizers regularly helps to lock in moisture and prevent dryness and itching.
Topical corticosteroids: These are special creams or ointments that doctors may prescribe to reduce redness, itching, and inflammation. They are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors: Another type of cream or ointment that doctors may recommend. They help to reduce inflammation and itchiness, especially in sensitive areas like the face and groin.
Antihistamines: Sometimes, doctors may prescribe antihistamines to help reduce itching and promote better sleep, especially if the itching is interfering with a good night’s rest.
Systemic immunomodulators:
IL-4/13 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors are two types of medications used to treat atopic dermatitis (eczema) in certain cases. Both IL-4/13 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors are used for people with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis who haven’t responded well to other treatments or have specific conditions that make them good candidates for these medications. These medications can have side effects, so it’s important to work closely with your health care provider who can monitor their usage and provide appropriate guidance throughout the treatment process. Let’s take a closer look at each of them:
IL-4/13 inhibitors: These medications work by blocking certain proteins in the body called interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13). These proteins play a role in the inflammation and immune response associated with atopic dermatitis. By blocking IL-4 and IL-13, these inhibitors help reduce the symptoms of eczema, such as itching, redness, and inflammation. Examples of IL-4/13 inhibitors include dupilumab, which is given as an injection, and is approved for use in both adults and children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.
JAK inhibitors: JAK inhibitors are a type of medication that targets a group of enzymes called Janus kinases (JAKs). JAKs are involved in the signaling pathways that contribute to inflammation in the body. By inhibiting JAKs, these medications help reduce inflammation and symptoms of atopic dermatitis. Examples of JAK inhibitors used for atopic dermatitis include upadacitinib. These medications are typically taken orally, in pill form.
- IL-31 inhibitors: These medications work by blocking certain proteins in the body called interleukin-31 (IL-31). These proteins play a role in the inflammation and immune response associated with itching and atopic dermatitis. By blocking IL-31, these inhibitors help reduce the symptoms of eczema, such as itching, redness, and inflammation. Examples of IL-31 inhibitors include nemolizumab, which is given as an injection, and is approved for use in patients with atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis.
Embark on your journey to radiant skin
Eczema is a chronic condition, often very severe, with periods of flare-ups and remission. Regular follow-up appointments are needed. Chapel Hill dermatology patients, who suffer from atopic dermatitis, can schedule an appointment with us here. A member of our elite dermatology team, including Dr. Weiss, a nationally recognized atopic dermatitis expert, will conduct a total evaluation of your skin. Our elite dermatology specialists will explore the various treatment options so that we give you the best treatment for your eczema. Patients with atopic dermatitis, looking for a dermatologist near Hillsborough, Carrboro, Raleigh, Sanford, Mebane, Durham, Burlington, Cary, and Alamance, can call our center for dermatology in Chapel Hill today to learn more.

